CHAPTER 2: ACCOUNTING EQUATION
 What is an asset?
What is an asset?
An asset
- is anything of value that is owned by or owed to the business
- can be used to earn profits
- is a resource controlled by the business and is beneficial to it (e.g.
cash, stock, bank account, furniture & fittings)
- can be classified according to how quickly the items can be turned into
cash (i.e. their liquidity)
- A current asset
is an asset that is normally expected or intended to be converted
into cash or used up within the accounting period
- A long-term/fixed asset is an asset
that normally takes more than the accounting period to be converted into
cash or to be used up
 What is a
liability?
What is a
liability?
A liability
- is anything that the business owes to external parties
- is a claim on the business assets by an outside party (e.g. creditors,
accounts payable)
- A current liability is a liability
that is asked to be repaid by external parties within one accounting period
- A long-term liability is a liability
that external parties are willing to be repaid for more than one accounting
period
 What is owner's
equity or capital?
What is owner's
equity or capital?
- refers to the claim on the assets of a business by the owner or the internal
party of the business
- is the difference between the assets and liabilities of a business
- When the owner takes out assets (i.e. cash or office supplies etc) from
the business for his/her own use, this is known as drawings
- Since drawings reduce the owner's claim on the assets of
the business, it can be seen as the opposite of capital or 'negative' capital
 Differences between Revenue
& Expenses
Differences between Revenue
& Expenses
|
Revenue
|
Expenses
|
| Refers to what a business earns as a result of the sale
of goods and/or services |
Refers to the cost of goods and services used to earn revenue |
| Increases the capital of the business |
Decreases the capital of the business |
|
E.g. Thames' tuition agency's revenues would be the tuition fees collected
from students
E.g. G2000 is a multinational fashion retailer that earns its revenues
through the sale of clothes
|
E.g. Thames' tuition agency will advertise for students.
Hence, the cost of advertising is an expense to the business |
 The Accounting Equation
The Accounting Equation
- is built from the accounting entity concept that regards the business
and the owner of the business as two separate persons or entities
- looks at all the transactions from the viewpoint of the business
- is stated as Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity (or Capital)
 Effects of Business Transactions
on the Accounting Equation
Effects of Business Transactions
on the Accounting Equation
- Besides the owner bringing in capital to the business, there are many
transactions that would have an effect on the accounting equation
- The example below will show you how various business transactions will
have an effect on Thomas's business - Thomas Delivery Services
- Thomas starts his own business, Thomas Delivery Services, by investing
S$20,000 of his own savings into the business. He opens a bank account in
the name of his business.
-
From the business' viewpoint, the business (Thomas Delivery
Services) has an asset - a bank account, and the source of that asset
is capital (the owner's claim on the asset)
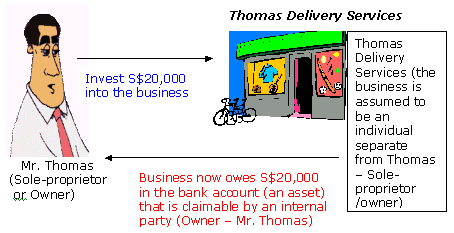
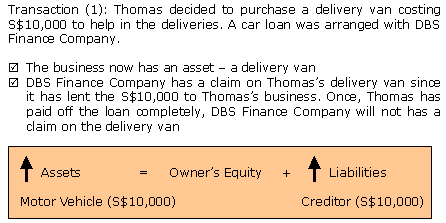
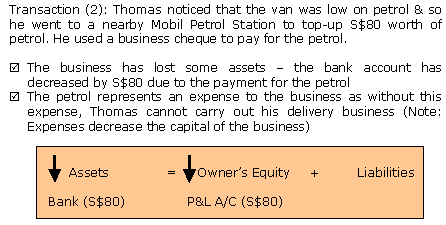
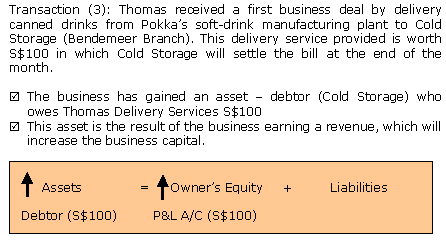
- The impact on the accounting equation is:



Alan Goh Jiang Wee © 2001-2002


![]() What is an asset?
What is an asset?![]() What is a
liability?
What is a
liability?![]() What is owner's
equity or capital?
What is owner's
equity or capital?
![]() Differences between Revenue
& Expenses
Differences between Revenue
& Expenses![]() The Accounting Equation
The Accounting Equation![]() Effects of Business Transactions
on the Accounting Equation
Effects of Business Transactions
on the Accounting Equation



